Conjunctiva is a thin, transparent membrane that covers the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of this membrane that can be infectious or noninfectious.
Types of Conjunctivitis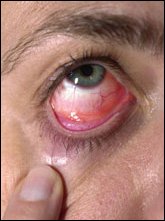
Among the non-infectious types, the most common type of conjunctivitis is allergic type. This eye problem is also seen in people with seasonal allergies and may also be caused by intolerance to substances such as cosmetics, perfume, or drugs.This type of conjunctivitis is not contagious. Infectious conjunctivitis has two types. The viral type that is caused by a virus and usually involves cold and sore throat. The second type, or bacterial conjunctivitis, is usually caused by bacteria such as staphylococci and streptococcus. The severity of the infection depends on the type of bacteria involved.
Signs and Symptoms of Conjunctivitis
The most common symptom of conjunctivitis is red eye that is caused by inflammation. Symptoms of different types of conjunctivitis can be summarized as follows:
• Allergic Conjunctivitis: Usually affects both eyes and causes itching and redness with tearing and swollen eyelids. The patients may also have runny nose because of allergies.
• Viral Conjunctivitis: usually affects one of the eyes and may eventually spread to the other eye. Other symptoms include severe tearing, watery discharge and red eye.
• Bacterial Conjunctivitis (Microbial): Affects both eyes and causes stringy discharge that may cause the lids to stick together, especially after sleeping. Other symptoms include swelling of the conjunctiva, redness and tearing. This type of conjunctivitis usually affects only one eye, but may spread easily to the other eye.
Conjunctivitis Diagnosis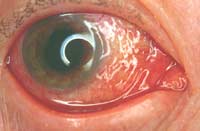
Conjunctivitis is diagnosed during a routine eye exam using a slit lamp microscope. In some cases, cultures are taken to determine the type of bacteria causing the infection.
Prevention of Conjunctivitis
Since viral and bacterial conjuctivities are contagious and easily transmitted, prevention has a very important role in preventing the transmission of infection to the other eye of the patient as well as other people. For effective prevention, you should pay attention to the following points:
• Wash your hands regularly and avoid touching or rubbing your eyes.Most viruses that cause conjunctivitis spread through hand-to-eye contact by hands or objects that are contaminated with the infectious virus.
• Never share your towels
• Never share your eye cosmetics such as eye liners, eye shadow and ...
• Never share your eye drops
• Avoid swimming (Some bacteria can be transmitted through water)
• Disinfect tables and countertops at your work or home
• Avoid shaking hands
• Do not use common tissue paper to clean your eye and then keep it to reuse. It is better to use a tissue paper.
Conjunctivitis Treatments
• Allergic Conjunctivitis: cool compresses and artificial tears sometimes relieved is comfort in mild cases. In more severe cases, non-steroidal anti inflammatory medications and antihistamines may be prescribed. Some patients with persistent allergic conjunctivitis may also require topical steroid drops.
• Viral Conjugate Virus: Like the common cold, there is no cure for viral conjunctivitis; however, the symptoms can be relieved with cool compresses and artificial tears. For the worst cases, topical steroid drops may be prescribed to reduce the discomfort from inflammation. Viral conjunctivitis usually resolves within 3 weeks.
• Bacterial Conjugate: Usually treated with antibiotic drops or ointments.
Last Point
Although conjunctivitis is usually a mild infection and does not pose a problem, it can sometimes be severe and cause more serious eye problems, so you should see an ophthalmologist if you experience any of the conjuctivitis symptoms.